Control robotic arm joint angle
1. Introduction to API
power_off()
Function : Uninstall the robotic arm.
After uninstallation, the robot arm will no longer maintain its posture and can be moved by hand.
Parameter explanation:
- Return value: None
power_on()
Function: Enable the robotic arm. After enabling, do not move the robotic arm by hand.
Parameter explanation:
- Return value: None
2. About code
Code path:~/jetcobot_ws/src/jetcobot_ctrl/scripts/ctrl_joints.ipynb
Create three new buttons to control the robotic arm reset, enable, and uninstall functions.
def on_button_clicked(b):
with output:
print("Button clicked:", b.description)
if b.description == 'Reset':
reset_joints()
elif b.description == 'Power_on':
mc.power_on()
b.icon = 'check'
button_power_off.icon = 'uncheck'
elif b.description == 'Power_off':
mc.power_off()
b.icon = 'check'
button_power_on.icon = 'uncheck'
Create seven new sliders to control the six joints and grippers of the robot arm.
def on_slider_S1(angle):
print("J1:", angle)
mc.send_angle(1, angle, g_speed)
def on_slider_S2(angle):
print("J2:", angle)
mc.send_angle(2, angle, g_speed)
def on_slider_S3(angle):
print("J3:", angle)
mc.send_angle(3, angle, g_speed)
def on_slider_S4(angle):
print("J4:", angle)
mc.send_angle(4, angle, g_speed)
def on_slider_S5(angle):
print("J5:", angle)
mc.send_angle(5, angle, g_speed)
def on_slider_S6(angle):
print("J6:", angle)
mc.send_angle(6, angle, g_speed)
def on_slider_S7(angle):
print("G7:", angle)
mc.set_gripper_value(angle, g_speed)
Create a new slider to control the movement speed of the servo.
slider_speed = widgets.IntSlider(description='Speed:', value=50, min=1, max=100, step=1, orientation='horizontal')
def on_slider_speed(value):
global mc, g_speed
g_speed = value
print("speed:", value)
widget_speed = widgets.interactive(on_slider_speed, value=slider_speed)
Reset the joint angles of the robotic arm.
def reset_joints():
if button_power_off.icon == 'check':
mc.power_on()
time.sleep(1)
mc.send_angles([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -45], 50)
mc.set_gripper_value(100, 50)
slider_S1.value = 0
slider_S2.value = 0
slider_S3.value = 0
slider_S4.value = 0
slider_S5.value = 0
slider_S6.value = -45
slider_S7.value = 100
slider_speed.value = 50
button_power_on.icon = 'check'
button_power_off.icon = 'uncheck'
Create a camera display window to read the camera image in real time and display it.
imgbox = widgets.Image(format='jpg', width=640, height=480, layout=widgets.Layout(align_self='center'))
model = 'Start'
def camera():
global model
capture = cv.VideoCapture(0)
capture.set(cv.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 640)
capture.set(cv.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 480)
while capture.isOpened():
try:
_, img = capture.read()
if model == 'Exit':
break
imgbox.value = cv.imencode('.jpg', img)[1].tobytes()
except:
break
with output:
print("capture release")
capture.release()
Create a close button to end the program and release resources.
button_close = widgets.Button(description='Close_Camera', button_style='danger')
def button_close_Callback(value):
global model
model = 'Exit'
with output: print(model)
button_close.on_click(button_close_Callback)
3.Run program
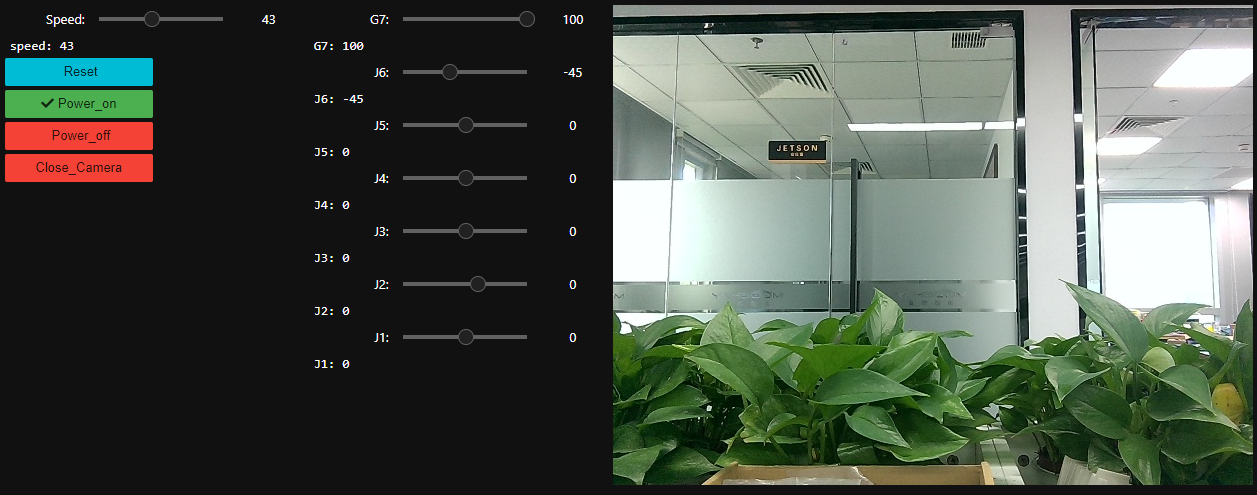
Click the Run Entire Program button on the Jupyterlab toolbar and scroll to the bottom.
You can see that the relevant control controls are displayed on the left and the camera display screen is displayed on the right.
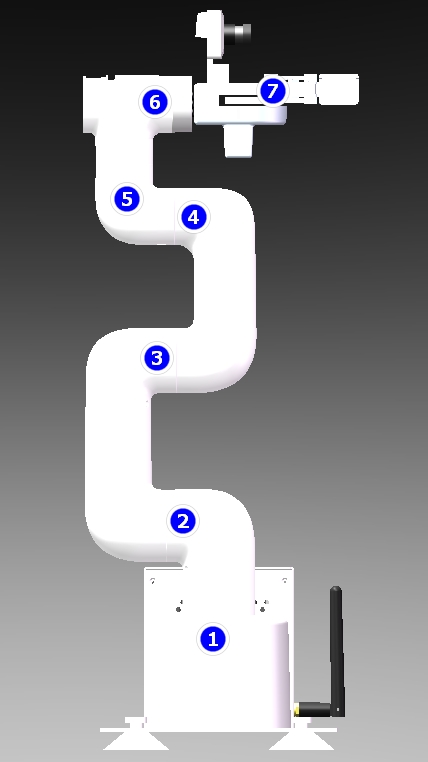
The corresponding positions of the robotic arm joints, are shown in the figure below.